Anyone looking at the NORAC signal aspect charts may have noticed that the familiar PRR dwarf position lights have a curve to them (or yaw) that can go both ways. For all four dwarf indications, Slow Clear, Slow Approach, Restricting and Stop, one will see two entries on the diagram chart, one with a left hand curve and one with a right hand curve. To the uninitiated this can be dismissed as having to do with clearances or which side of the track a dwarf signal is placed, but it actually represents a fairly early change by the PRR to make a more practical signal vs a more conceptually accurate signal.

The first PRR position light signals were designed as a replacement for semaphores. Version 1 or "tombstone" position lights (due to the shape of the backing) consisted of 4-lamp lines with an off-center pivot point that directly mirrored the shape and function of a semaphore blade. The position light dwarf signal was no different, but used two lamps to mimic the right to left sweep of a dwarf semaphore. Originally only three positions were provided, stop, low speed prepared to stop and low speed, again matching the function of the dwarf semaphore.
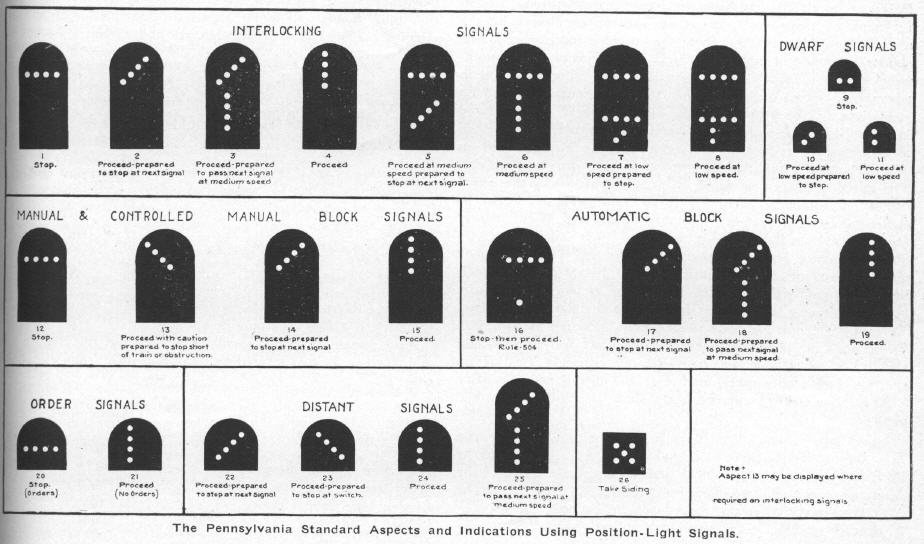
Between 1918 and 1925 the three lamp system with circular mounting became standard for high signals, but the dwarfs, unable to be simplified further, retained the design aesthetic of a semaphore blade sweeping out a curve. The one major change was that someone noticed that the 4-lamp PL dwarf could display the reverse \ for free and a distinction between "proceed expecting stop" and "proceed expecting obstruction" was able to be made. The result was the left-handed dwarf position light.
Made of cast iron by Union Switch and Signal, the left hand dwarf had bulb access hatches on both the straight and curved sides. The rest was a sealed unit with a small vent on the back.
This model of PL dwarf would go on to be installed at all the great PRR signaling achievements of the 1930's such as ZOO and HARRIS, however the march of progress is never satisfied and the desire to simplify the design merged with the desire to reduce confusion. The new dwarf would be reversed such that the curve would proceed in a high hand direction with the Restricting \ position being reduced in size compared to the Slow Approach / Position. The design was also changed to one with a single large rear access door, possibly enabled through advances in large gasket technology.


The new style position light proceeded to almost entirely replace the old, especially as the staffed interlocking towers and their electro-mechanical interlocking machines were replaced by CTC starting in the 1970's. By the 21st century left handed PL dwarfs were a rare sight with most appearing at those parts of Amtrak and Conrail territory that had escaped re-signaling since the 1930's. However while out at LINCOLN interlocking on Amtrak's Northeast Corridor in Metuchen, NJ, I spotted a left handed survivor governing movements out of the MoW yard.
Somehow escaping replacement in the early 90's when LINCOLN tower was closed and re-signaled, LINCIOLN's 5W dwarf is now one of the more accessible left-handed PL dwarfs, mounted on the side girder of the Lake St bridge for all to see.
Hopefully it will escape scrutiny and continue to perform its job for years to come.


















































